1. Saudi Arabia's investment advantages
Saudi Arabia has maintained its position as China's largest trading partner in West Asia and Africa for many years and is China's first 100 billion US dollar trading partner in the Middle East. In 2022, China and Saudi Arabia signed the "Comprehensive Strategic Partnership Agreement between the People's Republic of China and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia" and cooperation agreements in the fields of justice, education, energy, investment, and news to implement the docking of the "Belt and Road" initiative and Saudi Arabia's "Vision 2030" and promote the further development of bilateral relations.
Saudi Arabia's "Vision 2030" aims to get rid of the oil-dependent economic structure and seek economic diversification and sustainable development. To this end, Saudi Arabia has announced a series of strategies including national investment strategy, financial technology strategy, national intellectual property strategy, and national industrial strategy to encourage global investors to invest in Saudi energy and minerals, transportation, information and communications, health care, life sciences, industrial manufacturing, financial services, infrastructure and other fields, and to invest more than 3.2 trillion US dollars before 2030 to support economic transformation. At the same time, Saudi Arabia has improved its investment legal system, opened special zones and free economic zones, actively invested in infrastructure construction, and continuously improved the business environment, providing foreign investors with broad development space.
II. Saudi Foreign Investment Access Regulations
The Saudi Foreign Investment Law defines foreign natural persons, foreign legal persons, and Saudi legal persons directly or indirectly held by foreign capital as foreign investors. Foreign investors who intend to invest in Saudi Arabia need to comply with Saudi Arabia's industry restrictions and obtain a foreign investment license issued by the Saudi Ministry of Investment.
(I) Industry restrictions
The Saudi Supreme Economic Council publishes and regularly updates the negative list, and foreign investors are prohibited from investing in industries listed in the negative list. According to the latest version of the "Service Manual" issued by the Saudi Arabian Ministry of Investment in June 2023, the negative list prohibits foreign investors from investing in the following industries:
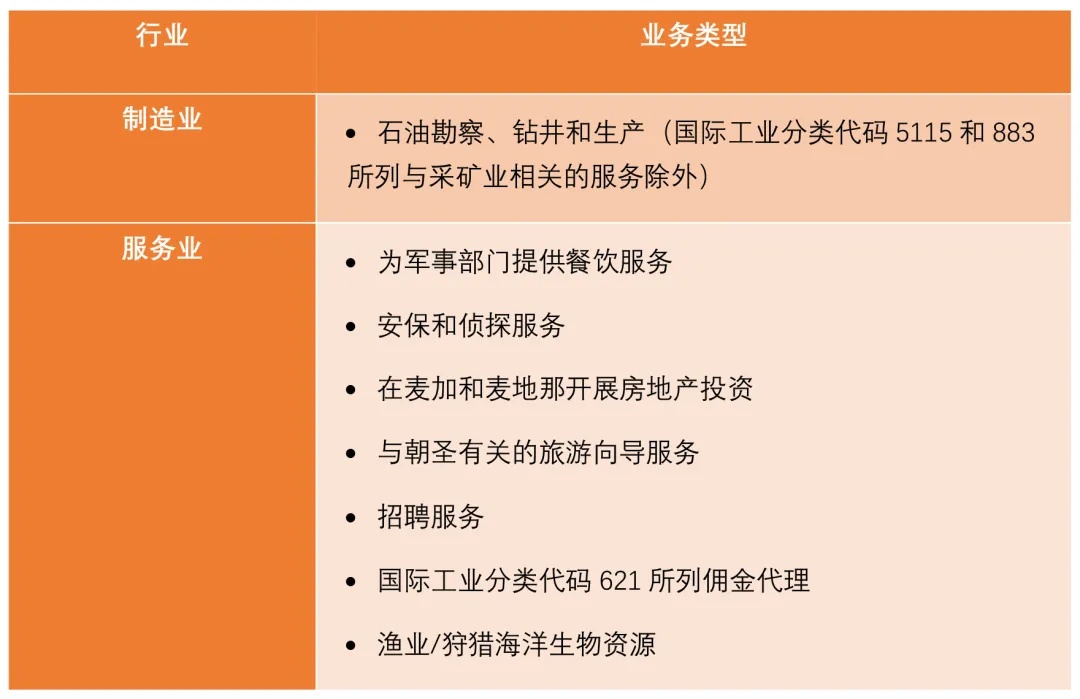
(II) Investment license and access requirements
Foreign investors investing in Saudi Arabia must strictly abide by the scope of permission on the investment license. There are 20 categories of Saudi investment licenses, each of which covers a variety of industries, such as service licenses (applicable to construction, information technology, tourism, training, medical care, insurance, reinsurance, education, advertising and media, logistics services, exhibition organization, catering and food services, financial services, aviation and loading and unloading services, etc.), industrial licenses (applicable to heavy industry, light industry, transformation industry, etc.), trade licenses, mining licenses, science and technology office licenses (applicable to the establishment of representative offices), etc.
Saudi Arabia has set entry requirements for foreign investors in some industries, such as minimum registered capital and minimum shareholding ratio of Saudi shareholders.
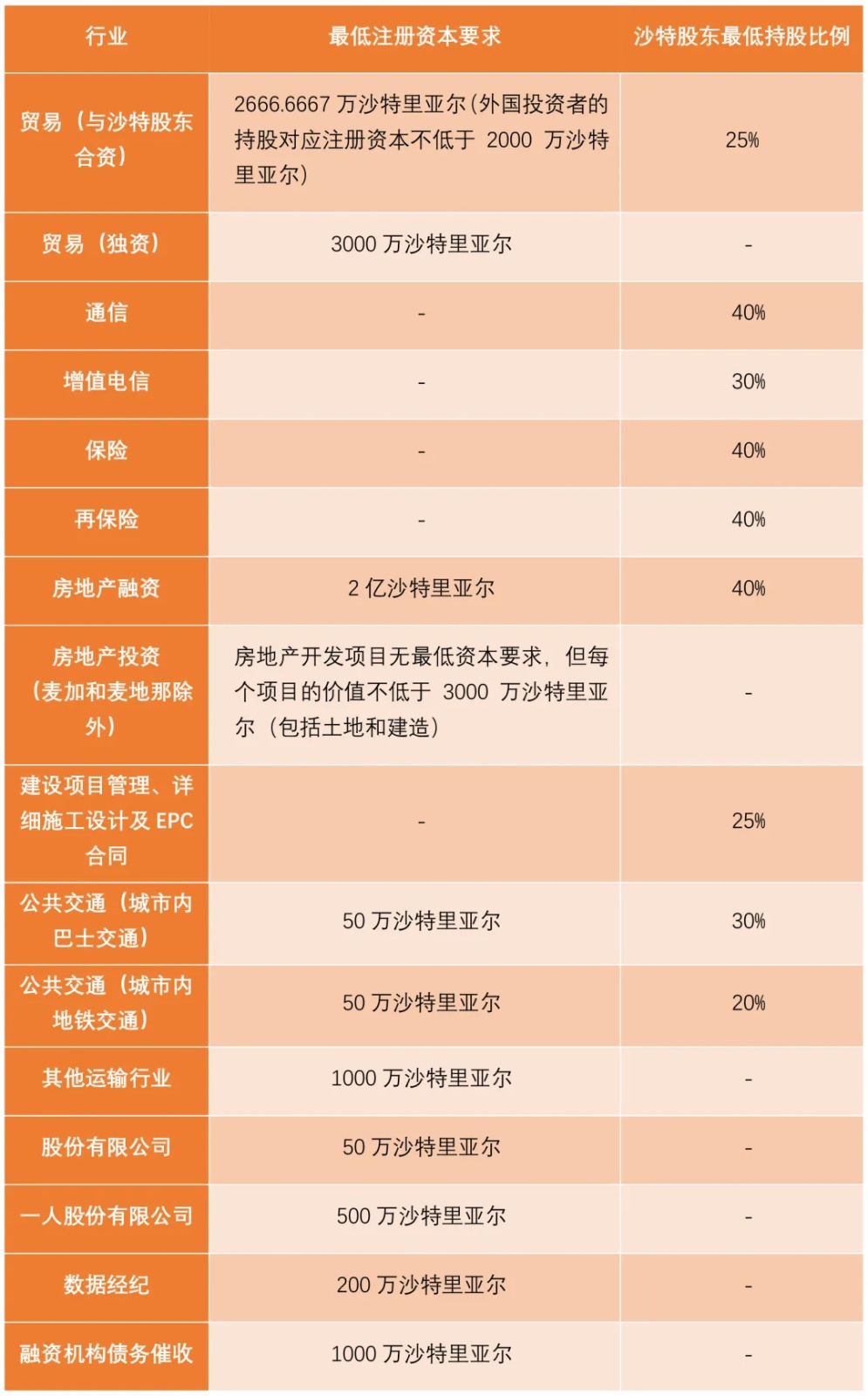
(III) Application requirements for major investment licenses
Based on our experience, the major investment licenses applied for by foreign investors are service licenses, industrial licenses and trade licenses. The following is a brief introduction to the application requirements for the three types of licenses.
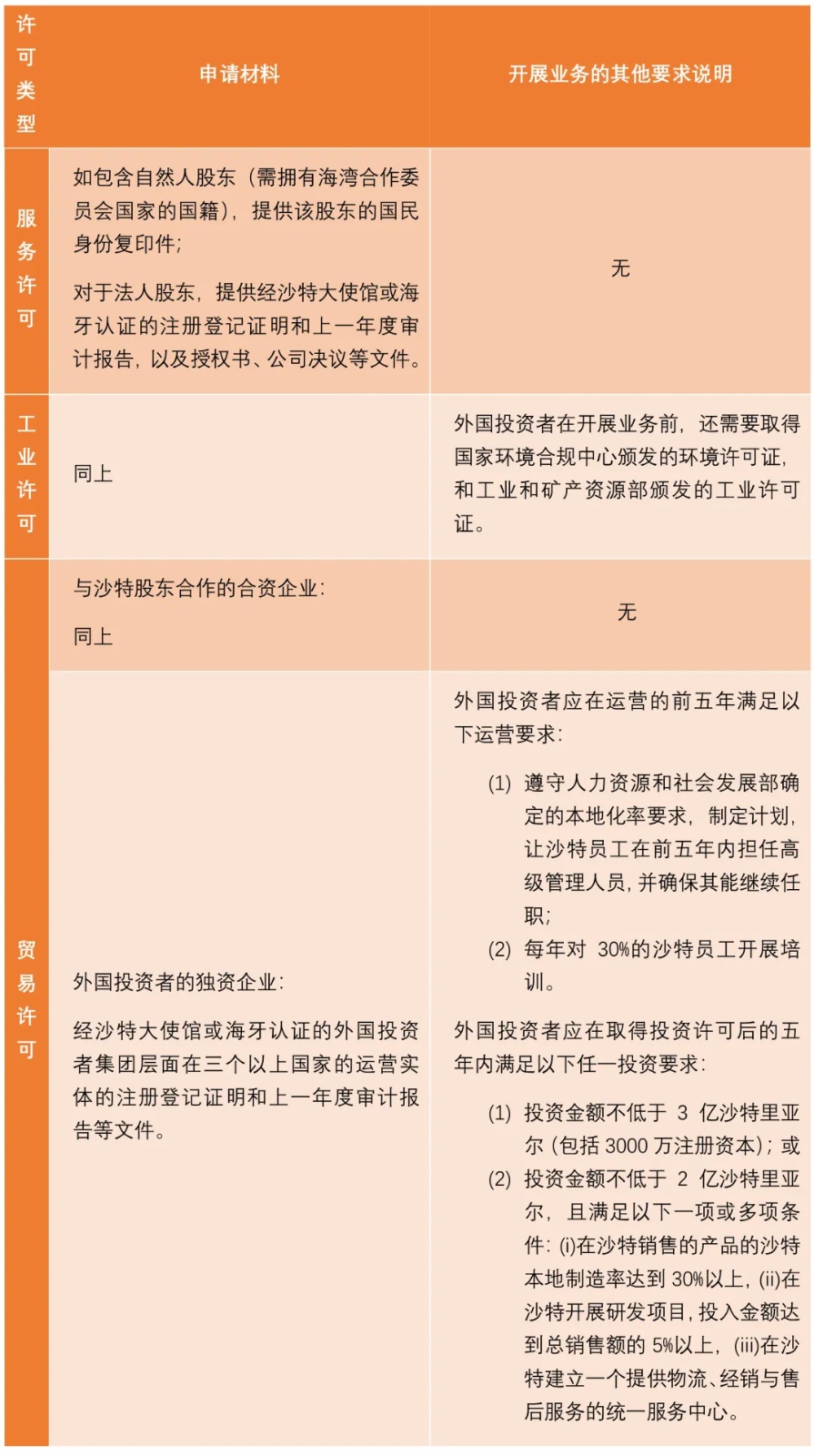
III. Saudi Arabian company establishment and governance regulations
(I) Entity forms of foreign-invested enterprises
According to Saudi Arabia's Foreign Investment Law and Company Law, foreign investors can establish general partnerships, limited partnerships, joint-stock companies, simplified joint-stock companies and limited liability companies to carry out commercial activities. From the perspective of the freedom of commercial activities, limited liability companies are currently the most popular investment form for foreign investors and can be established by one or more natural or legal persons.
Limited liability companies do not have a minimum registered capital requirement, but for limited liability companies established by foreign investors, the Saudi Arabian Ministry of Investment usually requires their registered capital to be no less than 500,000 Saudi riyals. In addition, limited liability companies also need to comply with the minimum registered capital requirements for applying for investment licenses in individual industries. In practice, Saudi Arabia often requires limited liability companies to pay up all registered capital within a certain period of time. According to our observation, this time limit is usually short. The Saudi Arabian Ministry of Investment often requires foreign investors to promise to pay up the registered capital within a few months after obtaining the investment license.
(II) Procedures for the establishment of foreign-invested enterprises
The procedures for foreign investors to establish a limited liability company in Saudi Arabia and conduct substantive business involve the following steps:
1. Approval and reservation of company name
Approval of company name is conducted through the website of the Saudi Arabian Ministry of Commerce. The approved company name will be reserved for 60 days.
2. Application for foreign investment license
Submit materials to the Saudi Arabian Ministry of Investment to apply for a foreign investment license.
3. Notarization and publication of articles of association
Prepare the company articles of association in Arabic and submit them to the Saudi Arabian Ministry of Commerce for approval. After the Ministry of Commerce approves them, the notary public will notarize the articles of association.
4. Business registration
Submit a series of materials including the notarized company articles of association to the Saudi Arabian Ministry of Commerce to complete the business registration.
5. Open and activate a bank account
In order to meet the paid-in capital requirements, the company shall open and activate a bank account within 90 days after the completion of the business registration.
6. Registration with various government departments
The company needs to register with the Chamber of Commerce (according to the Saudi Enterprise Registration Law, the company should complete the registration with the Chamber of Commerce. In addition, the company also needs to obtain the signature of the registered general manager of the Chamber of Commerce and go through the certification procedures for some business documents), the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development, the General Administration of Social Insurance, the tax authorities (Zakat, Taxation and Customs General Administration) and other government departments, and register the actual office address. In addition, the company also needs to register on government portals such as Mudad (employee salary management and compliance reporting platform), Muqeem (used to manage the company's desertification rate) and QIWA (used to manage employee residence permits) to carry out activities necessary for company operations such as signing labor agreements and managing employee visas.
7. Other operating licenses
The company should also obtain special licenses required to engage in business, such as an environmental license issued by the National Environmental Compliance Center and an industrial license issued by the Ministry of Industry and Mineral Resources before carrying out industrial activities.
(III) Corporate Governance of Foreign-Invested Enterprises
According to the Saudi Arabian Company Law, the corporate governance of a limited liability company is usually relatively simple, with only a two-tier governance structure of the General Assembly and the Manager/Manager Committee, excluding the Board of Directors, the Board of Supervisors, etc. The key points are as follows:
1. General Assembly
According to the Saudi Arabian Company Law, shareholders holding shares in a Saudi limited liability company are called partners, and partners shall enjoy corresponding voting rights according to their shareholdings. A limited liability company shall hold an annual general assembly within 6 months after the end of each fiscal year, and may hold an interim general assembly at the request of a partner representing more than 10% of the voting rights, a manager or the company's auditor.
The Saudi Arabian Company Law has made mandatory provisions on the voting ratio of resolutions of the general meeting of partners of a limited liability company. Amendments to the articles of association, capital increase or capital reduction require the consent of partners representing more than 75% of the voting rights before they can be passed. If the company wishes to stipulate drag-along rights and tag-along rights in the articles of association, the matter must also be approved by partners representing more than 90% of the voting rights.
2. Manager/Manager Committee
The daily business affairs of a limited liability company are decided and executed by the manager. The general meeting of partners can appoint one or more managers and decide on the decision-making method for establishing a manager committee. The Saudi Arabian Ministry of Commerce website lists hundreds of powers that the general meeting of partners can grant to the manager/manager committee, including but not limited to signing documents in the chamber of commerce, disposing of company property, applying for and transferring company trademarks, appointing and removing other company managers, establishing or closing bank accounts in the name of the company, opening branches, etc. The general meeting of partners can further clarify the contents of the powers that should be exercised by the manager himself, authorized to be exercised by others (i.e., acting according to the instructions of the manager), or fully authorized to be exercised by others. If a manager harms the interests of the company, in addition to the resolution of the general meeting of partners to remove the manager, more than one quarter of the partners can also sue the judicial authorities to remove the manager.
Saudi Arabia does not restrict the nationality of company managers, but foreigners who have not obtained residence permits and work permits may face obstacles when opening bank accounts for the company and opening government-related services such as the Chamber of Commerce and the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development. Considering the long processing period for residence permits and work permits, in practice, foreign investors usually hire local people as temporary managers to handle company registration-related matters first.
IV. Saudi Arabian Land System
(I) Land Acquisition
After obtaining an investment license issued by the Saudi Ministry of Investment, foreign investors have the right to own Saudi land and real estate. Nevertheless, foreign investors who purchase relevant land or real estate must still meet various conditions:
(1) obtain approval from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs;
(2) such land and real estate must not be located in Mecca and Medina;
(3) such land and real estate must be required for foreign investors to carry out investment activities;
(4) if the land and real estate are used to build factories, they must be located within the scope of approved industrial cities;
(5) the use of such land and real estate is limited to private housing, factories, office buildings, employee housing or warehouses.
(II) Land leasing
Foreign investors can lease land or real estate in Saudi Arabia. Lease agreements are usually registered through an online platform published by the Saudi Ministry of Housing, but the registration requirements for lease agreements signed for industrial land in industrial cities need to follow the special regulations of the Saudi Industrial Cities and Technical Zones Authority and each industrial city (such as Jubail Industrial City and Yanbu Industrial City may have special requirements). Without registration, the court will not recognize the validity of the lease agreement.
Land leases in Saudi Arabia usually have no time limit, but as an exception, the initial term of a lease agreement signed between a foreign investor and a government department shall not be less than 5 years. In practice, the initial term of a lease agreement signed between a foreign investor and a government department is usually 15-25 years, and the two parties can renew the contract to 50 years.
V. Basic Labor and Employment System in Saudi Arabia
(I) Employee Employment
Saudi companies hiring employees should sign written labor agreements with employees and pay different types of social insurance for employees of different nationalities. Saudi labor agreements are written in Arabic and include two types: open-ended labor agreements and fixed-term labor agreements. Only Saudi and GCC national employees can sign open-ended labor agreements, while employees of other nationalities can only sign fixed-term labor agreements. If the labor agreement does not stipulate a term, the term of the work permit obtained by the employee shall be deemed as the term of the labor agreement. If there is no renewal clause in the fixed-term labor agreement signed by Saudi or GCC national employees, and the company and the employee continue to implement the labor agreement after the expiration, the labor relationship between the two parties will be deemed to be renewed in the form of an open-ended labor agreement; if there is a renewal clause in the fixed-term labor agreement signed by the aforementioned national employees, and it has been renewed three times, or the employee has worked in the company for four consecutive years, the labor agreement renewed by both parties will automatically be converted into an open-ended labor agreement. The company can agree with the employee on a probation period, which usually shall not exceed 90 days, but can be further extended according to the written agreement between the company and the employee. The total probation period after extension shall not exceed 180 days (excluding public holidays and sick leave).
Saudi companies with more than 6 employees who intend to hire non-Saudi employees must comply with the Saudi labor law's requirements for the proportion of Saudi employees ("Saudiization rate"), and certain positions in the company (such as human resources managers) can only be held by Saudi nationals. The Saudi Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development divides the Saudiization rate of companies into five ranges: red zone (0-16.21%), light green zone (16.22-19.25%), green zone (19.26-23.11%), dark green zone (23.12-26.51%) and platinum zone(26.52-100%), each range has distinct differences in terms of employment benefits and employment restrictions. For example, companies in the red zone are not allowed to apply for or renew visas for foreign employees, while companies in the light green zone can renew work permits for eligible foreign employees, but are not allowed to apply for new visas.
(II) Employee dismissal
The labor relationship between Saudi companies and employees can be terminated due to mutual agreement (employees must provide written consent), unilateral dismissal by the company, unilateral resignation of employees, expiration of the labor agreement, employee retirement, or company closure. After the labor relationship is terminated, the company needs to pay the employee an end-of-service bonus, the amount of which depends on the employee's years of service. Specifically: 0.5 months' salary per year for the first five years, and 1 month's salary per year starting from the sixth year. If an employee voluntarily resigns, the end-of-service bonus will be reduced.
If a Saudi Arabian enterprise intends to unilaterally dismiss an employee, it shall deliver a written notice of dismissal to the employee in advance according to the time agreed in the labor agreement ("notice period"), and the notice shall state the legitimate reasons for dismissing the employee. For employees who have signed an open-ended labor agreement, if the applicable remuneration system is a monthly salary system, the notice period shall not be less than 60 days; if the employee is subject to other remuneration systems, the notice period shall not be less than 30 days. For employees who have signed a fixed-term labor agreement, the Saudi Arabian Labor Law does not stipulate the minimum requirement for the notice period, but in practice it is usually not less than 30 days. The enterprise may pay the employee a compensation in lieu of advance notice, and the amount of the compensation shall be equal to the employee's salary during the notice period.
The Saudi Arabian Labor Law does not stipulate the legitimate reasons for the enterprise to dismiss an employee. In practice, after a labor dispute occurs, the court will exercise discretion based on the facts. If the court determines that the enterprise has no legitimate reason to dismiss an employee, the enterprise shall pay compensation to the employee, and the compensation varies depending on the type of labor agreement signed by the employee. If the labor agreement signed by the employee is a fixed-term labor agreement, the compensation amount is the full salary for the remaining term of the contract; if the labor agreement signed by the employee is an open-ended labor agreement, the compensation amount is the employee's service years * 15 days' salary, but shall not be less than the employee's 2 months' salary.
If an employee has disciplinary issues stipulated in the Saudi Labor Law, the company can immediately dismiss the employee without paying the end-of-service bonus. The disciplinary issues clearly stipulated in the Saudi Labor Law include:
Employees attack their employers, supervisors or any of their superiors during or for work reasons;
Employees fail to perform the main obligations agreed in the labor agreement or fail to comply with legal instructions, or despite written warnings, deliberately fail to comply with notices on work and employee safety posted in conspicuous places by the company;
Behavior that can prove that the employee has committed misconduct or violated good faith;
Employees deliberately act or fail to act with the intention of causing significant losses to the company, but the company should report the incident to the competent authorities within 24 hours after discovering it;
Employees falsify any information materials to obtain work;
Employees are absent from work for more than 30 days or more than 15 consecutive days without reason within a year (but the company should send a written warning to the employee when the cumulative absence is 20 days or the continuous absence is 10 days);
Can prove that the employee abused his power for personal gain;
Can prove that the employee leaked business secrets.
VI. Antitrust Approval
If a foreign investor intends to invest in Saudi Arabia in the form of a new joint venture or merger and acquisition, and the relevant transaction meets the following conditions at the same time, it is necessary to submit a declaration to the Saudi Arabian General Competition Authority before the transaction is completed in accordance with the requirements of the Saudi Arabian Competition Law.

VII. Conclusion
Saudi Arabia's stable political environment, friendly and open business policies, good development potential and its gradually rising important position in the global economic system have attracted global investors to invest in Saudi Arabia. However, it is worth noting that Saudi Arabia is currently in the early stages of reform and opening up, and the law may change further at any time. With the continuous introduction or improvement of relevant systems, Chinese investors may also be subject to the requirements of new legal rules. In addition, Saudi Arabia's desertification rate and other requirements have imposed many restrictions on foreign investment. We recommend that Chinese investors fully understand Saudi Arabia's foreign investment legal environment before investing in Saudi Arabia, consult professionals for professional advice, and escort their investment.

Customized overseas services for Chinese enterprises
Helping Chinese companies to expand overseas with less worries

